IP Protocol
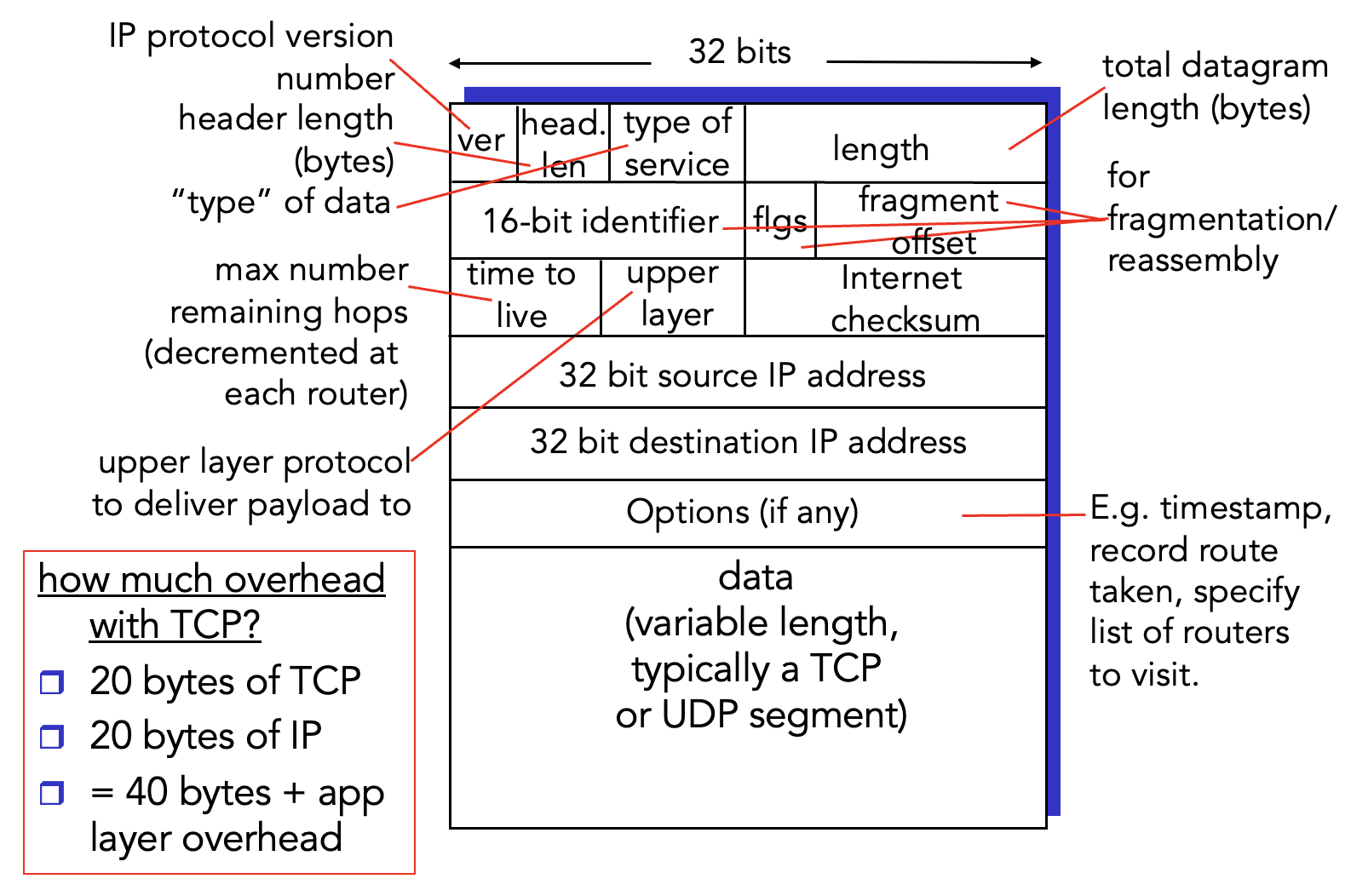
IP Datagram
Network layer header
- Things that changes: TTL and 16-bit identifier + fragment offset
- Other things mostly stay the same
Fragmentation & Reassembly
Network links have MTU (Max Transfer Size)
Large IP datagram divided within net
- One datagram becomes several datagrams
- Reassemble only at final destination
- IP header bits used to identify and order related fragments
This lowers the probability of bit flips because the packet is smaller, net gain
High bandwidth
low bit error probability send one giant packet
Low bandwidthhigh bit error probability fragment into small packets
Example:
4000 byte datagram with MTU = 1500 bytes
- 1480 bytes in data field
- Offset interval is 1480 / 8 = 185
(original offset is 1480, but divide by 8 because not enough bits)
IP Addressing
IP address: 32-bit identifier for host, router, interface
Interface: connection between host/router and physical link
- Router's have multiple interfaces
- Host has one interface
- IP addresses associated with each interface
Each IP address has a
- Subnet part (high order bits)
- A subnet device interfaces with same subnet part of IP address, can physically reach each other without intervening router
- Host part (low order bits)
CIDR
Classless InterDomain Routing
- Subnet portion of address of arbitrary length
- Address format
a.b.c.d/xwherexis # bits in subnet portion of address
Example:
11001000 00010111 00010000 00000000 <-------- subnet ---------><--- host---> 200.23.16.0/2323 bits for subnet, 9 bits for host
This supportsdevices within the same subnet
Getting an IP Address
Gets allocated portion of its provider ISP's address space
- Hard-coded by system admin in a file (static)
- DHCP: Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol: dynamically get address from server
Example:
Alice's IP address121.36.6.13
Bob's IP address121.36.7.11
Are they in the same subnet? Depends on the subnet mask length.
ISPs get IP addresses through ICANN
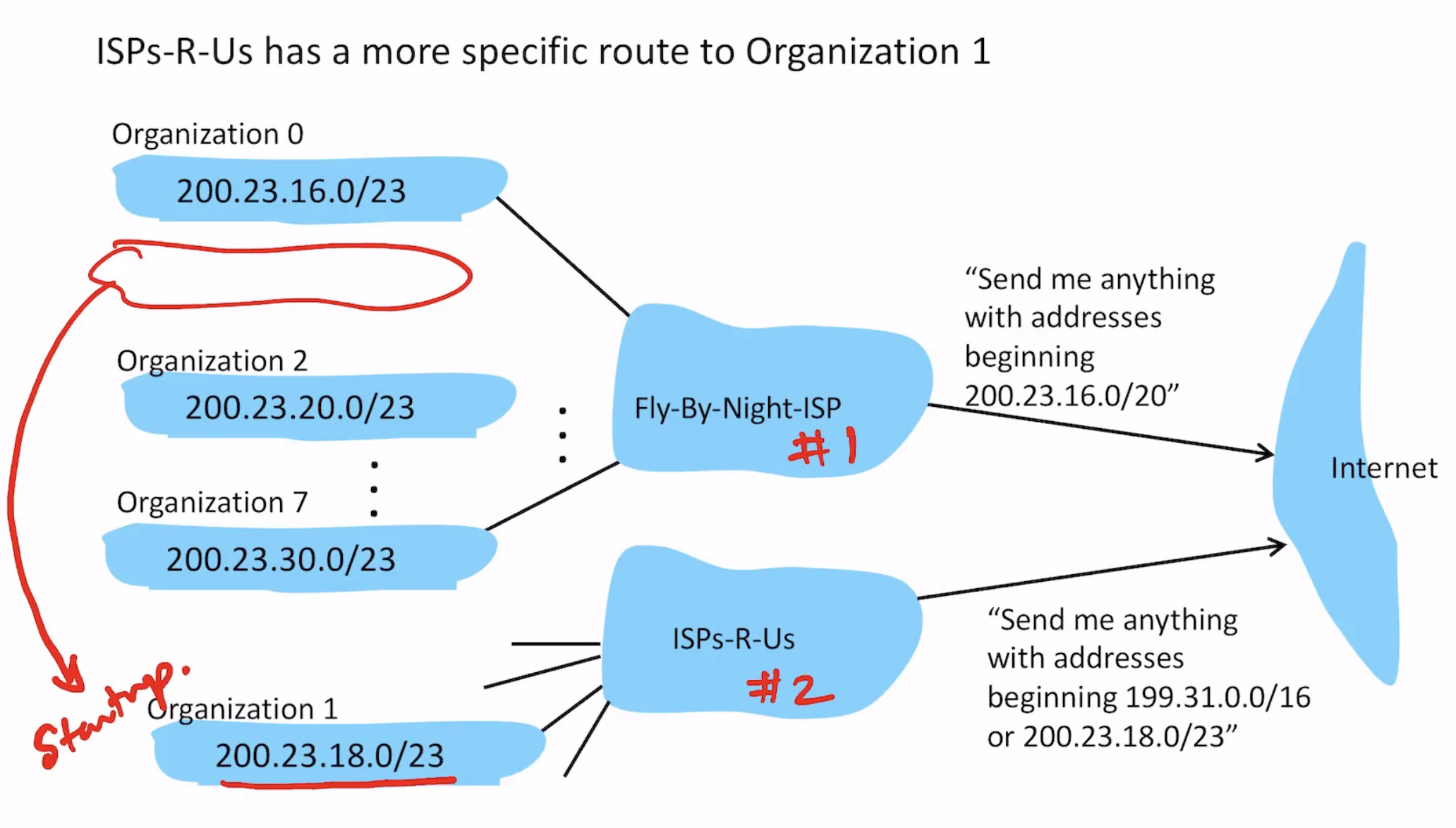
Hierarchical Addressing
Hierarchical addressing allows efficient advertisement of routing information.
- ISP advertises to the internet
- A tree: 1 ISP, 20 bits for host -> 8 organizations, each with 23 bits for host
Upon changing ISP from Fly-By-Night-ISP (#1) to ISPs-R-Us (#2)
- ISP#1 cannot encode "give me all these IP addresses EXCEPT one" in forwarding table
- ISP#1 doesn't change anything, continues to advertise the same thing
- ISP#2 has 23 bits for host (as compared to the original 20), so it will have the longest prefix match
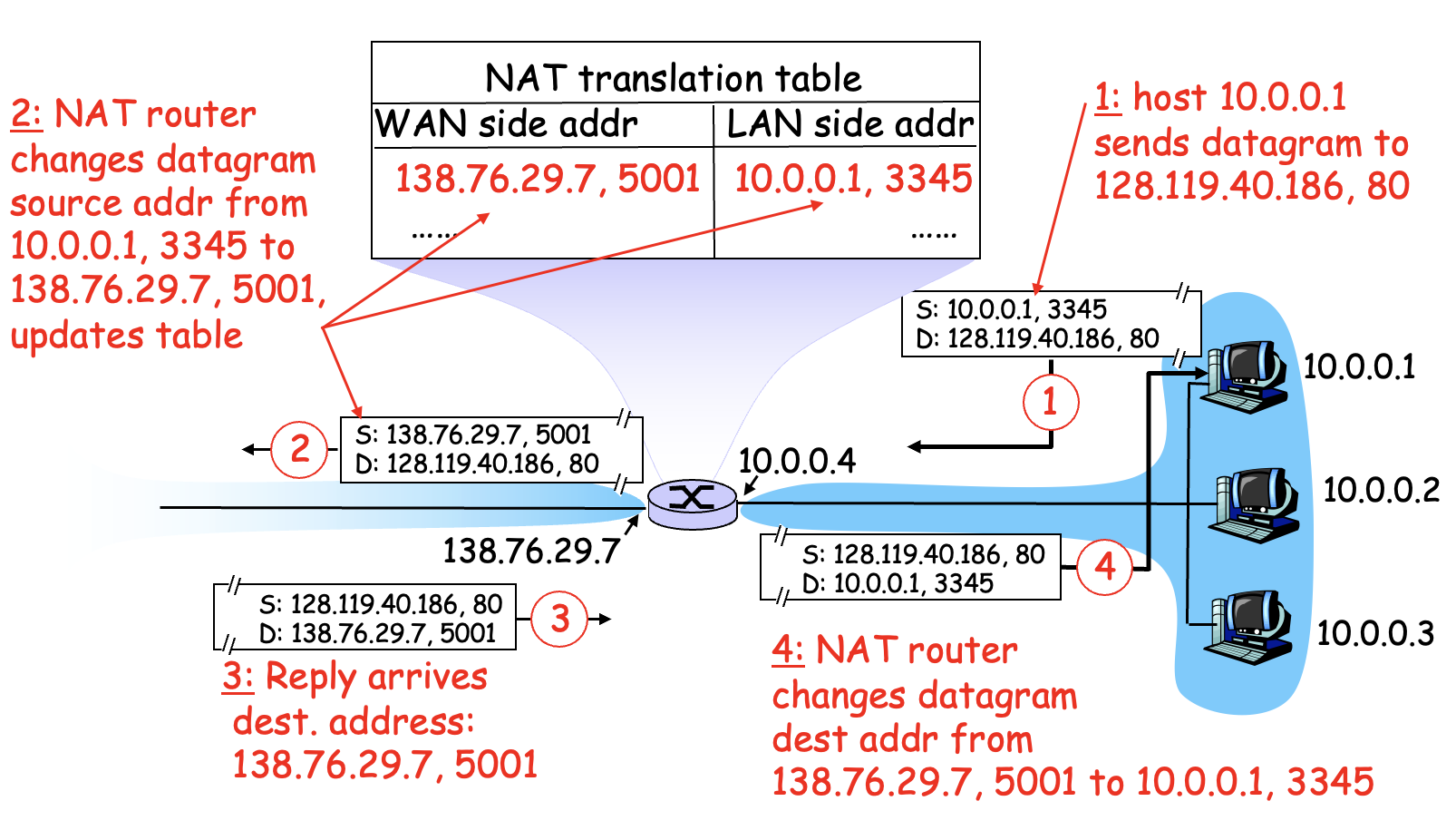
Network Address Translation (NAT)
All datagrams leaving local network have same single source NAT IP address, different source port numbers. Router maintains a redirection table, mapping a port number to the source port number.
Keeps that ports 5001 is for port 3345 on client side
Has to go into transport layer
16-bit port-number field (60,000 simultaneous connections with a single LAN-side address)
Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP)
Used by hosts and routers to communicate network-level information
- Error reporting: unreachable host, network, port, protocol
- Echo request/reply (used by ping)
An ICMP message contains type, code plus first 8 bytes of IP datagram causing error
IPv6
Initial Motivation: 32-bit address space soon to be completely allocated
Additional motivation:
- Header format helps speed processing/forwarding
- Header changes to facilitate QoS
IPv6 datagram format:
- Fixed-length 40 bytes header
- No fragmentation allowed
IPv6 Header:
- Priority: identify priority among datagrams in flow
- Flow Label: identify datagrams in same “flow.” (concept of“flow” not well defined).
- Next header: identify upper layer protocol for data
Other changes from IPv4:
- Checksum: removed entirely to reduce processing time at each hop
- Options: allowed, but outside of header, indicated by "Next Header" field
- ICMPv6: new version of ICMP
- Additional message types (e.g. "packet too big")
- Multicast group management functions
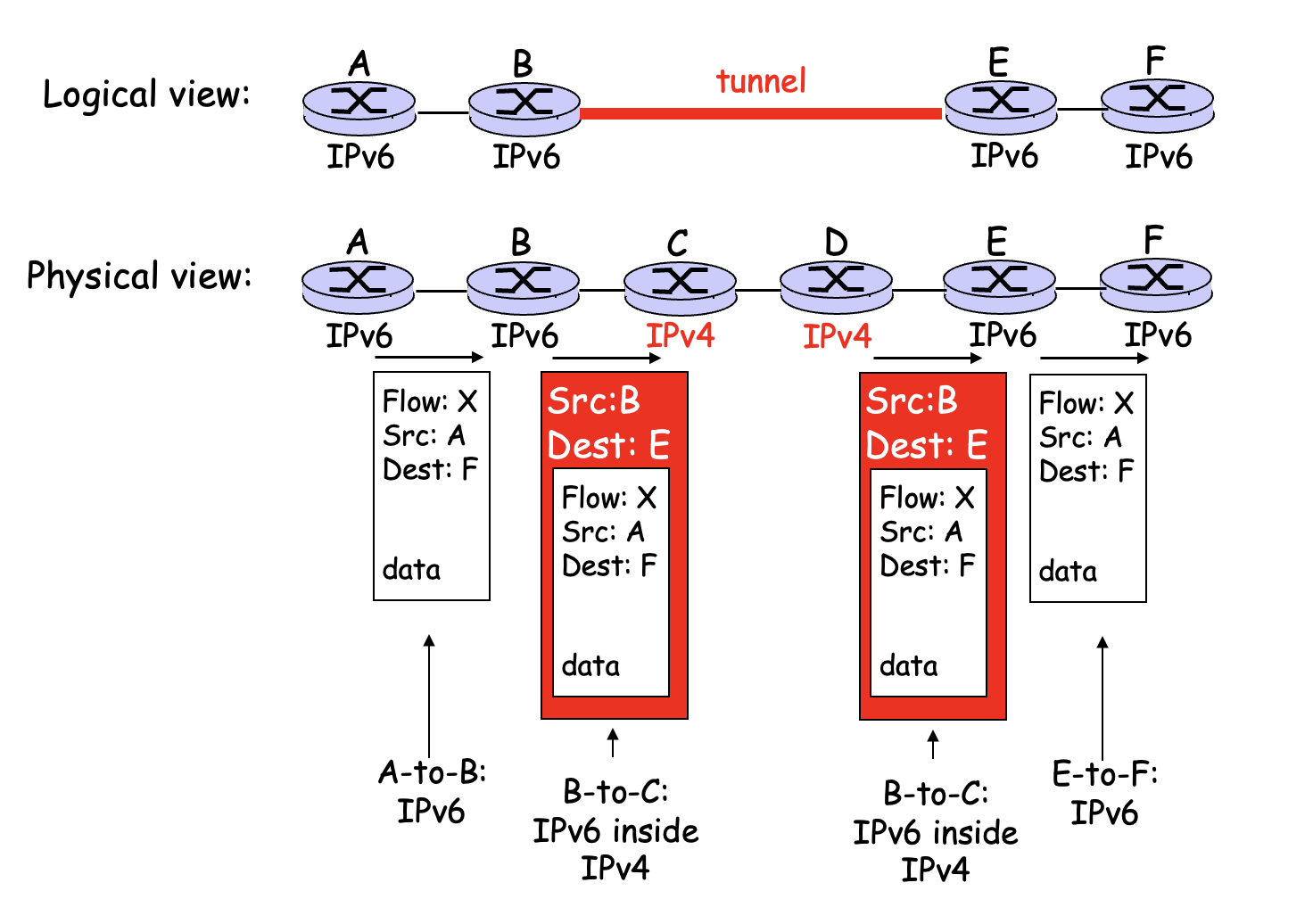
Tunneling
Transition from IPv4 to IPv6
- IPv6 carried as payload in IPv4 datagram among IPv4 routers